Forecasting Short-Term Urban Dynamics: Data Assimilation for Agent-Based Modelling
Forecasting Short-Term Urban Dynamics: Emerging Research and Challenges
Nick Malleson, Tomas Crols, Jon Ward, Andrew Evans
Schools of Geography & Mathematics, University of Leeds, UK
nickmalleson.co.uk
surf.leeds.ac.uk
dust.leeds.ac.uk
These slides: http://surf.leeds.ac.uk/presentations.html
How many people are there in Trafalgar Square right now?
We need to better understand urban flows:
Crime – how many possible victims?
Pollution – who is being exposed? Where are the hotspots?
Economy – can we attract more people to our city centre?
Health - can we encourage more active travel?
Achieve this through agent-based modelling smart cities?
Results
... but: lots of exciting developments at Leeds
Outline
Emerging research initiatives
What we see as the main chllenges
Would like feedback...
Leeds Institute for Data Analytics (LIDA)
Established 2014. 31 centres, programmes and projects (£43.2M)
Over 150 researchers and data scientists
Aspiring to be the premier data analytics centre in the UK
Overarching themes:
Understanding health and human behaviour
Social and environmental problems


Smart Cities Hub
Understanding and Quantifying Uncertainty in Individual-Based Models for Smart City Forecasts
Smart Cities Hub
Understanding and Quantifying Uncertainty in Individual-Based Models for Smart City Forecasts
Smart Cities Hub
Understanding Input Data Requirements for Successfully Modelling Cities
How much information about a city do we need to simulate it within acceptable levels of uncertainty?
Method:
Simple hypothetical city ABM
Generate 'truth' data
Take noisy samples from 'truth'
How much data do we need?
Agent-Based Urban Modelling

Current Research
Simulating Urban Flows (surf)
3 year research project funded by the UK ESRC
Modelling a small town, using real footfall counters (more on this next...)
One of the aims: calibrate an urban ABM using streaming data
Turns out this is really hard!
Agent-Based Urban Modelling

New project: Data Assimilation for Agent-Based Models (dust)
5-year research project (€1.5M)
Funded by the European Research Council (Starting Grant)
Started in January
Main aim: create new methods for dynamically assimilating data into agent-based models.
Divergence
Complex systems
One-shot calibration
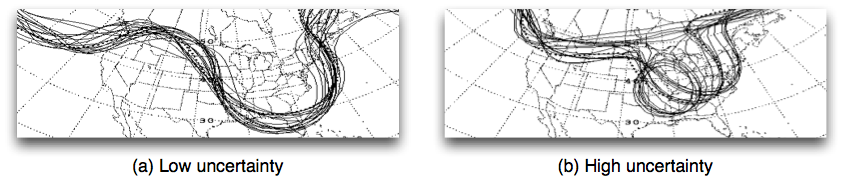
Nonlinear models predict near future well, but diverge over time.
Divergence
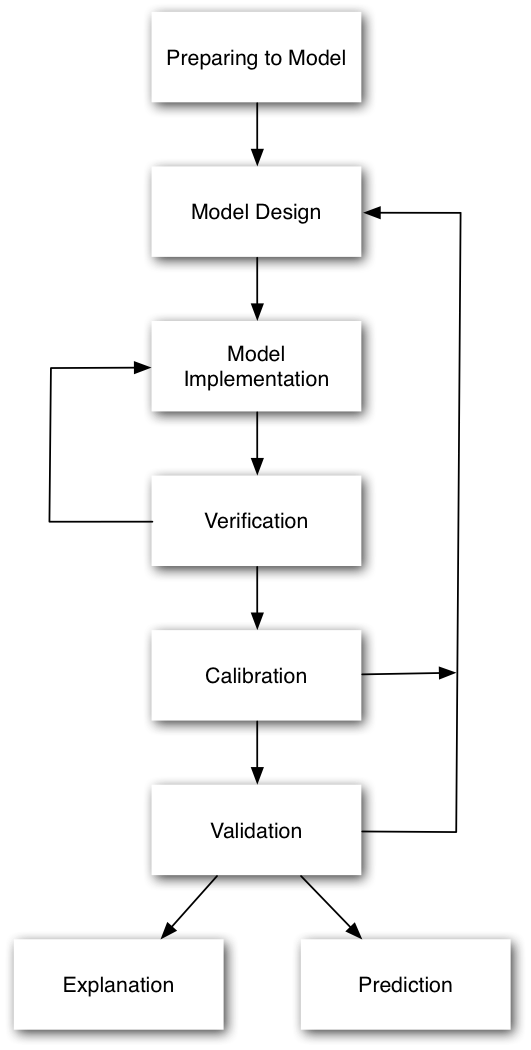
Drawback with the 'typical' model development process
Waterfall-style approach is common
Calibrate until fitness is reasonable, then make predictions
But we can do better:
Better computers
More (streaming) data
Methodological gap
Dynamic Data Assimilation
Used in meteorology and hydrology to constrain models closer to reality.
Try to improve estimates of the true system state by combining:
Noisy, real-world observations
Model estimates of the system state
Should be more accurate than data / observations in isolation.

DDA: How?
One example: Ensemble Kalman Filter (EnKF)
Broad literature, but generally tied to mathematical models (e.g. differential equations and linear functions)
Working with a mathematician to do the hard work!
In all its glory: Ward et al., (2016)
Advantages
Similar to Kalman Filter (best in class)
But better for nonlinear systems
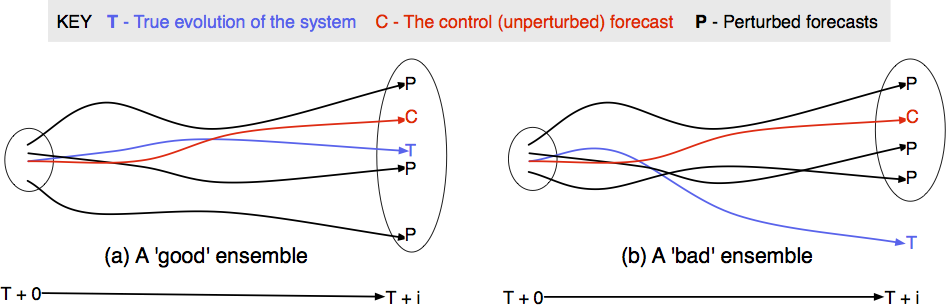
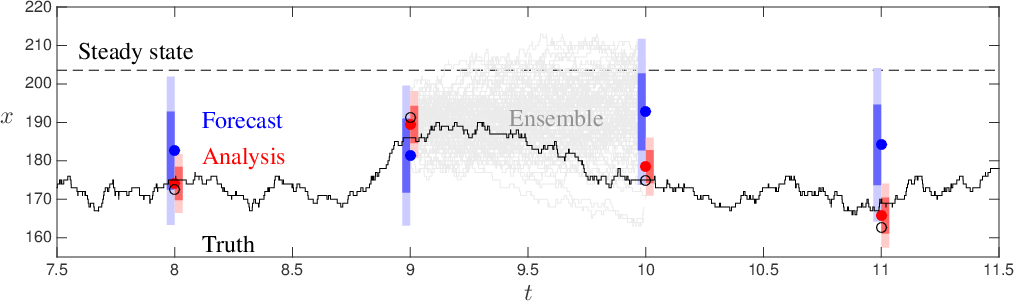
Ensemble Kalman Filter - Basic Process
1. Forecast.
Run an ensemble of models (ABMs) forward in time.
Calculate ensemble mean and variance
2. Analysis.
New 'real' data are available
Integrate these data with the model forecasts to create estimate of model parameter(s)
Impact of new observations depends on their accuracy
3. Repeat
Ensemble Kalman Filter (EnKF)
Outline
Challenges
Data Wrangling (standardising and automating datasets)
Recognising and understanding patterns
Supporting decision-making and risk management through simulation (developing applications)
Human and machine interaction in the city
Ethical and social implications of Smart Technologies
Conclusion
Lots of new smart cities / agent-based modelling work
Leeds Institute for Data Analytics
Alan Turing Institute
A couple of examples...
Opportunity: Fully-Funded PhD Scholarships
Deadline: 16 April 2018. Start: October 2018
Fully-funded (fees and stipend) for four years
1. Developing Model Ensembles and Emulators for Next-Generation City Simulation
2. Agent-Based Modelling of Smart Cities
Forecasting Short-Term Urban Dynamics: Data Assimilation for Agent-Based Modelling
Forecasting Short-Term Urban Dynamics: Emerging Research and Challenges
Nick Malleson, Tomas Crols, Jon Ward, Andrew Evans
Schools of Geography & Mathematics, University of Leeds, UK
nickmalleson.co.uk
surf.leeds.ac.uk
dust.leeds.ac.uk
These slides: http://surf.leeds.ac.uk/presentations.html